SHREE LEARNING ACADEMY
Privilege Escalation
Privilege escalation happens when a user gains higher levels of permissions, access, or privileges than what they were originally granted by an organization. This can happen either by mistake or due to an administrative error, but typically it refers to the deliberate exploitation of a system in order to gain unauthorized access.
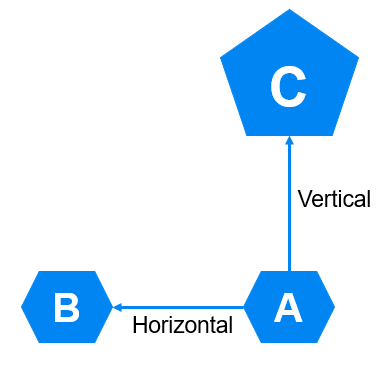
Weaknesses in the operating system can be exploited for privilege escalation. Typically, a hacker will use a tool to take advantage of a programming vulnerability or buffer overflow, which can potentially grant the attacker either temporary or permanent access to the administrator group. The type of attack where a low-level user or access is elevated to a higher level of access is referred to as vertical privilege escalation. On the other hand, there are situations where privilege escalation is achieved by stealing identity or compromising credentials, for example, through keystroke capturing or password cracking. When an attacker switches to another user account in order to gain higher access, this type of attack is referred to as horizontal privilege escalation.
To summarize, vertical privilege escalation is about accessing accounts that have greater privileges and permissions. Where as, horizontal privilege escalation is about accessing accounts that have near to similar privileges to the attacker's account.
Security Measures
Privilege escalation constitutes a security breach as it violates authorization restrictions and may also involve a breach of authentication. To prevent or halt privilege escalation, it's crucial to keep all operating systems updated with patches provided by the vendor. Moreover, it's important to configure auditing and monitoring mechanisms to detect signs of privilege escalation, such as multiple unauthorized attempts to perform user account management or accessing resources beyond an authorized level.
There are multiple strategies that can be employed to prevent privilege escalation, including:
- Keeping operating systems and software up-to-date with the latest security patches to minimize the risk of vulnerabilities that could be exploited for privilege escalation.
- Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts user permissions to only what is necessary for their job duties, thereby reducing the potential for users to escalate their privileges.
- Enabling multifactor authentication to make it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
- Regularly reviewing and updating user access privileges to ensure that users have only the access required for their job, and nothing more.
- Monitoring user activities for indications of suspicious behavior, such as multiple attempts to access resources beyond their authorized level.
- Deploying endpoint protection solutions like firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to identify and prevent attacks.
- Educating users about the best security practices, such as creating strong passwords and avoiding opening suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Test Yourself
Take Free Quiz
Watch our Video Tutorial